17-4 PH stainless steel
About 17-4PH Stainless Steel
17-4 PH is a martensitic precipitation - hardened stainless steel. It’s known for its corrosion resistance and high levels of strength and hardness, especially when heat treated. 17-4 can be heat treated to a variety of hardness and toughness levels, allowing users to customize post-sintering properties of the alloy to suit a wide variety of applications, including:
- Manufacturing machinery
- Chemical processing
- Food processing
- Pump components
- Valving
- Fasteners
- Jigs and fixtures
BMD + 17-4 PH
The ability to use 17-4 PH with the Studio System’s extrusion-based metal 3D printing process (Bound Metal Deposition™ or BMD™) makes it easy for designers and engineers to print 17-4 parts on-demand in their office or lab. Teams can iterate quickly on prototype parts and achieve complex geometries that have not been possible with traditional manufacturing methods. These new capabilities, as well as a cost-effective solution for printing parts in low volume (think: custom one off or replacement parts), are especially important for applications requiring 17-4 PH.
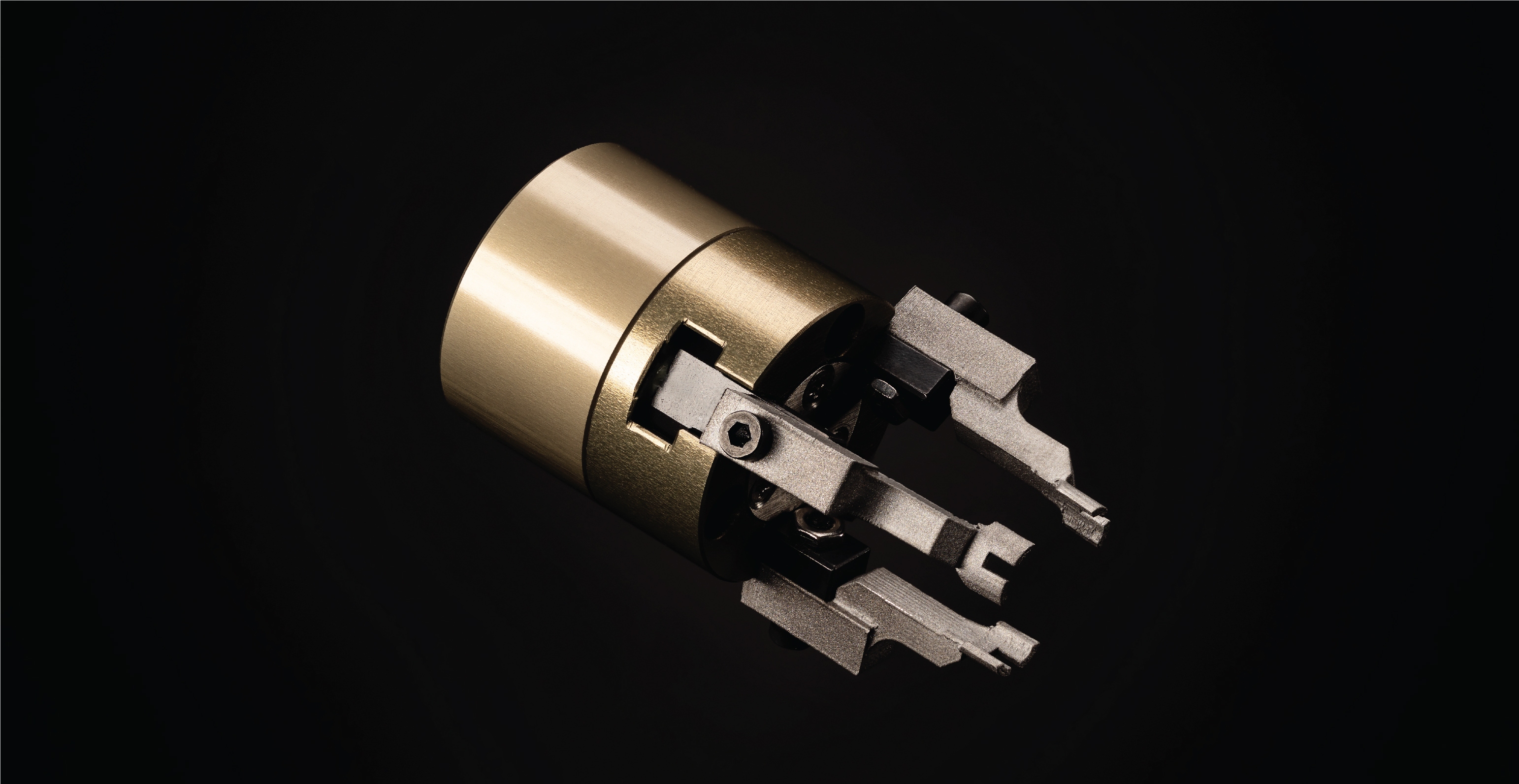

End Effectors
About the part
End effectors are a common component on manufacturing and assembly lines. These end effectors commonly require complex custom geometry to fit to the gripper they are being used with, as well as be able to interact with the environment in the desired way. The end effectors commonly need to change when the environment changes, for example when the parts being assembled change. In order to keep manufacturing lines running replacing broken or newly required designs with haste is essential.
With these specific end effectors the part being handled is very small, requiring similarly small end effectors. With the high resolution required, the 250 µm high resolution nozzle of the Studio System is the perfect manufacturing method. These end effectors would be very difficult to machine and very costly to Direct Metal Laser Sinter.
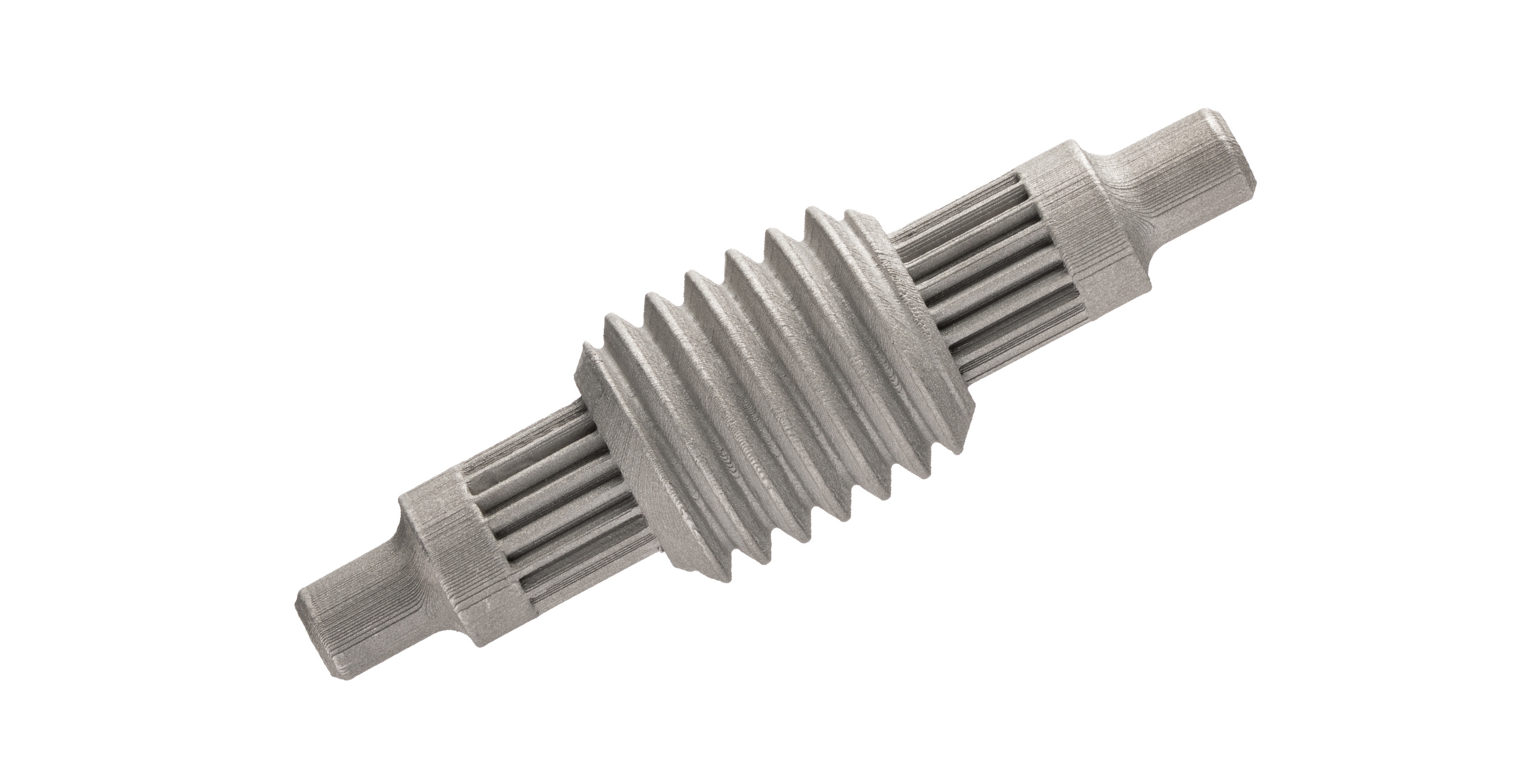

Roller Screw
About the part
Roller screws are an essential component of linear roller screw actuators, providing high force output with excellent precision control and speed. Often a great choice for replacing costly, high maintenance hydraulic actuators, roller screws are commonly found in applications like power plants where high force, speed, and position are required.
The complex threading and gearing integrated into this part make it extremely difficult and expensive to prototype. When designing a roller screw, testing and iteration is an essential part of the design process to ensure that the roller screws are performing to the desired specification of the actuator. With BMD, design teams are able to print and iterate on roller screw designs quickly in office, leading to a better designed product.
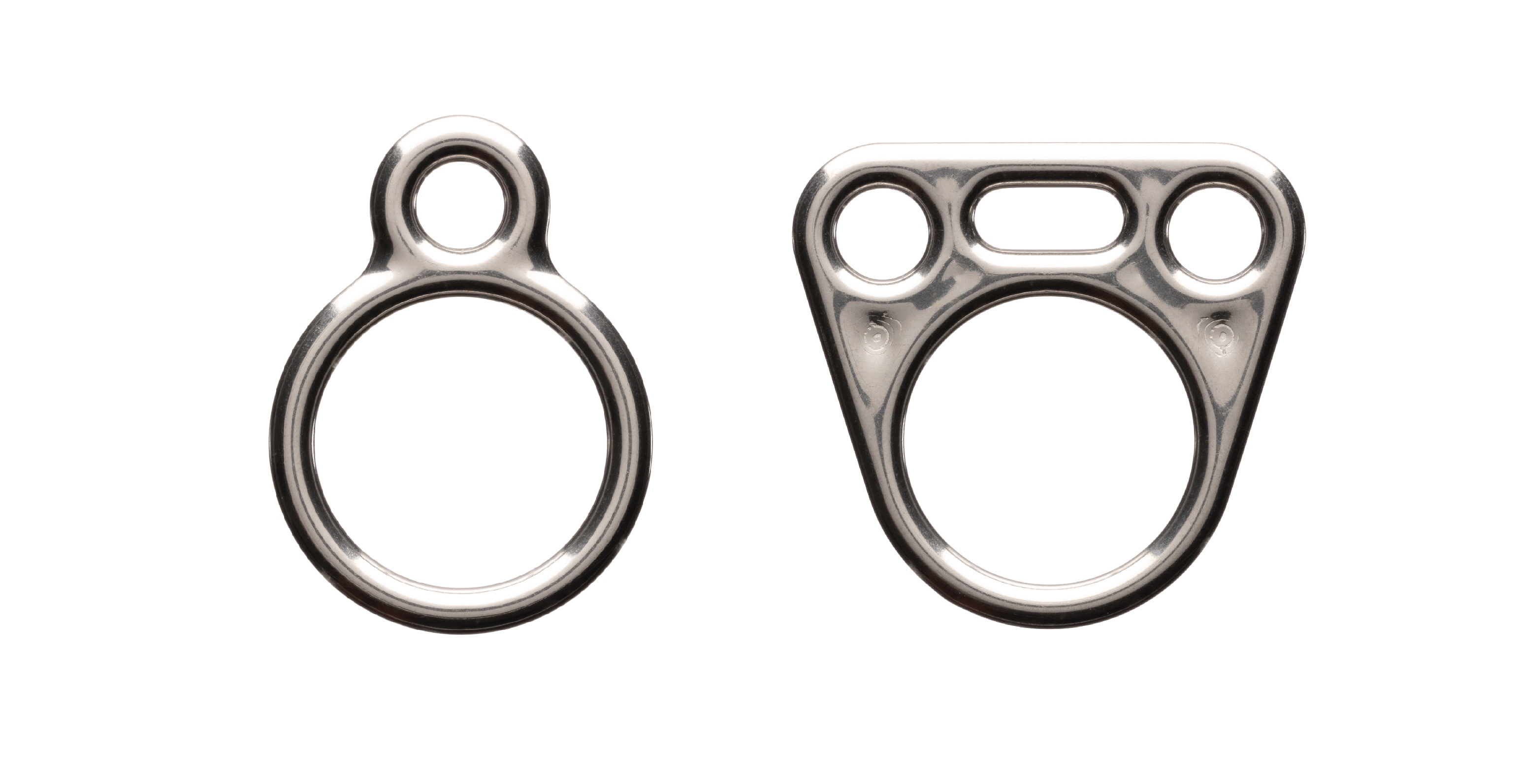

Parachute rings
About the part
Parachute rings are a critical component in the successful deployment of parachutes. If these rings fail to operate perfectly, they can result in hard parachute openings or a malformed canopy opening. These rings must be smooth on all sides to be able to efficiently slide down the parachute line during deployment.
These parts are difficult to fabricate due to their necessity for completely rounded edges throughout the ring, rendering laser and water cutting fabrication incompatible. Traditionally, parachute rings are fabricated with time consuming, hand fabrication and welding techniques. However with BMD, these parts can be printed in a variety of geometries and finished to the desired surface smoothness with ease.
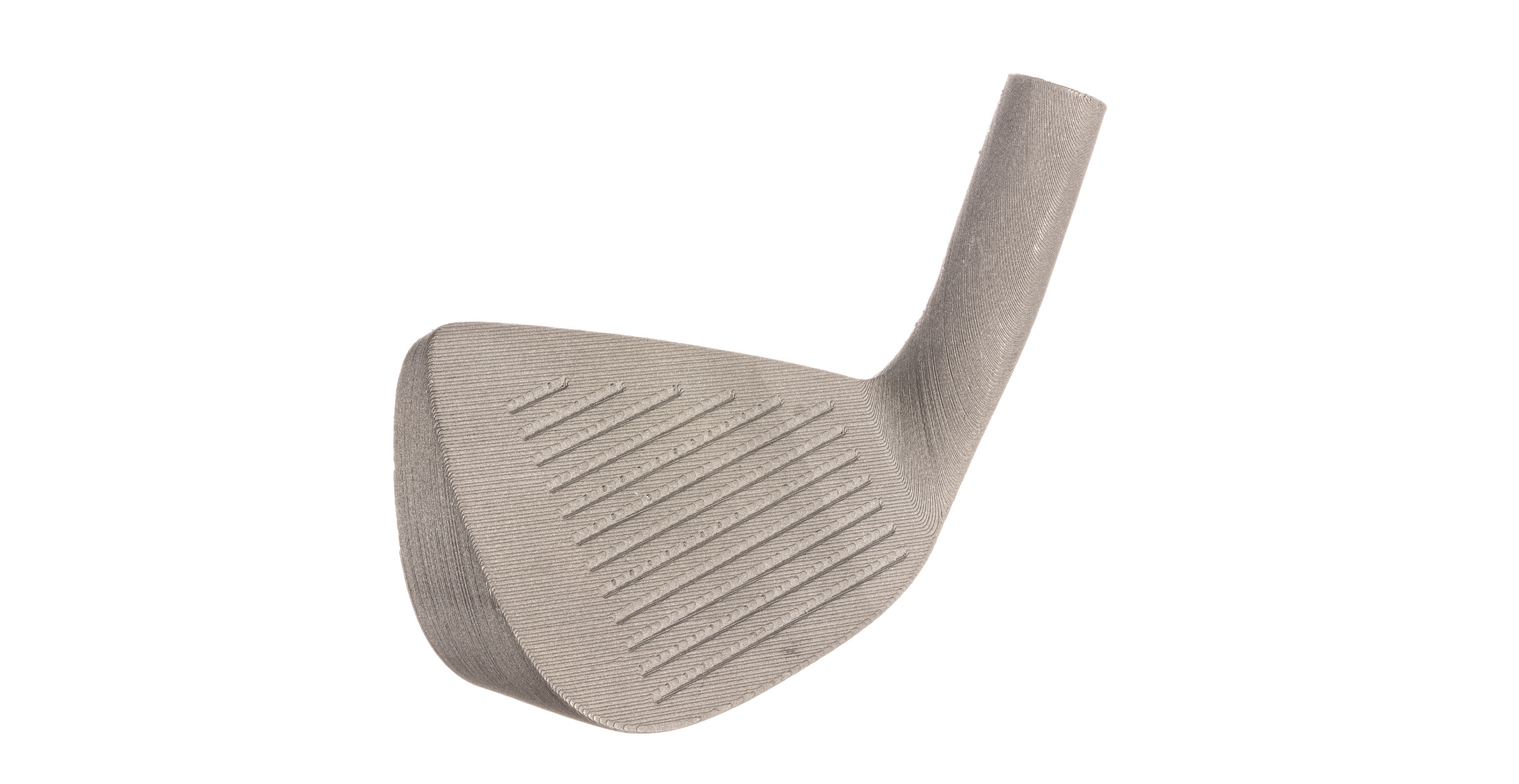

Golf Clubs
About the part
Golf club design is constantly evolving—from being carved out of wood in the 16th century, to today where clubs are cast or forged out of a variety of metals. Clubs have nearly endless design possibilities, including contact face surface area and shape, cavity shape and depth, club angle, bounce angle, groove shapes, patterns and depths, weight and many more. All of these factors and more must be considered when designing a club.
Considering the vast array of variables, prototyping and testing are an essential part of the golf club design phase. With the ease of use of the Studio System, teams are able to design, prototype, test, and iterate on multiple designs in as short as a week. This allows for teams to go through more design cycles to ensure clubs perform as intended.
Bound Metal Deposition makes metal 3D printing more accessible than ever before—allowing an entirely new generation of golf clubs to be produced. With designers freed from the boundaries of traditional manufacturing and production costs flat, low volume manufacturing of one-off highly custom clubs can be individually tuned to each golfer’s swing.
17-4 PH stainless steel is currently available for use with the Studio System. It is one of the six core materials in active development—including 316L (available now), Alloy 625, H13 tool steel, Copper, and AISI 4140.